
4.3 FACTORING A DIFFERENCEOF SQUARES AND CUBES

I) REVIEW: CONJUGATE OF A BINOMIAL
To find the conjugate of a binomial, you switch the signbetween the two terms
Positive Negative
Negative Positive
Ex: Find the Conjugate:

Q: WHAT HAPPENS WHEN YOU MULTIPLY ABINOMIAL WITH ITS CONJUGATE?
Ex: Expand the following
1. The middle two terms will always cancel each other out
2. The first and last terms are always perfect squares
3. The middle sign is always a subtraction

EX: INDICATE WHAT THE MISSING TERMS ARE:
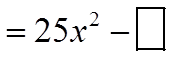
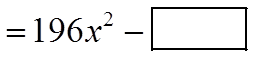
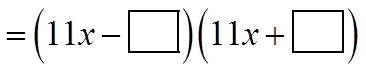
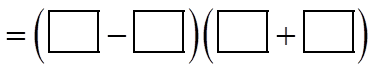
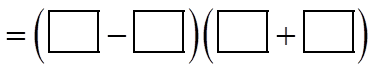

II) FACTORING A DIFFERENCE OF SQUARES
Difference Subtraction
Difference of Squares Subtraction of two perfect squares

When you multiply a binomial with its conjugate, theproduct will be a “difference of squares”

EX: FACTOR COMPLETELY
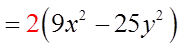
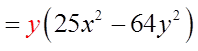
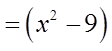
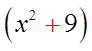
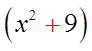

EX: FACTOR COMPLETELY


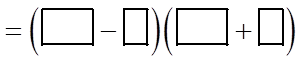
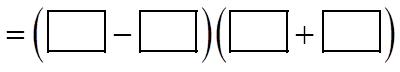
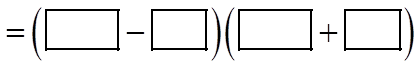

CHALLENGE: FACTOR
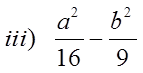
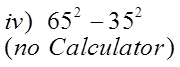
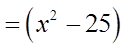
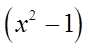
Can’t Factor!! Not a Difference
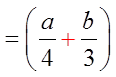
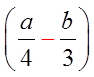

FACTORING DIFFERENCE OF CUBES:
Expand the following:
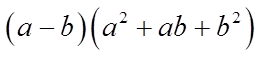
Combine Like-Terms
Some of the terms willcancel each other out
So the formula for thedifference of cubes is:
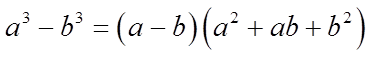

Ex: Given that “p” is a prime number, solve for “x”:
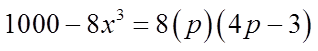
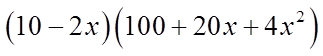
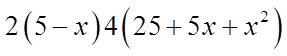
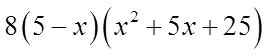
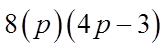
Let “p” equal to 5 – x
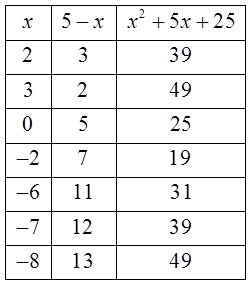
So “x’ is equal to –8 andthe prime “p” is 13

HOMEWORK: